Applying Lidar technology in air pollution monitoring
Lidar is an effective technique for finding and monitoring air pollution emission sources. By providing precise and thorough data, this technology assists managers in developing plans to minimise pollution emissions.
Vietnam has long used air monitoring equipment, instruments, and procedures, both manually and periodically, as well as automatically and continuously. However, monitoring technology is measured chiefly and calculated through the operation of urban low-level monitoring stations.
When heat convection causes pollution to urban dwellers, the process of transferring pollution from other sources and into the higher air layer has yet to be tracked or estimated.
Finding the source using satellite cloud photos does not ensure continuity and is not very persuasive because the pollution problem has yet to be assessed.
Faced with practical issues of air pollution monitoring, the unit conducted research and discovered that countries around the world have been using Lidar technology (Light Detection And Ranging) to monitor and evaluate high-altitude pollution parameters, as well as calculate the source of pollution spread in high-altitude air to urban pollution.
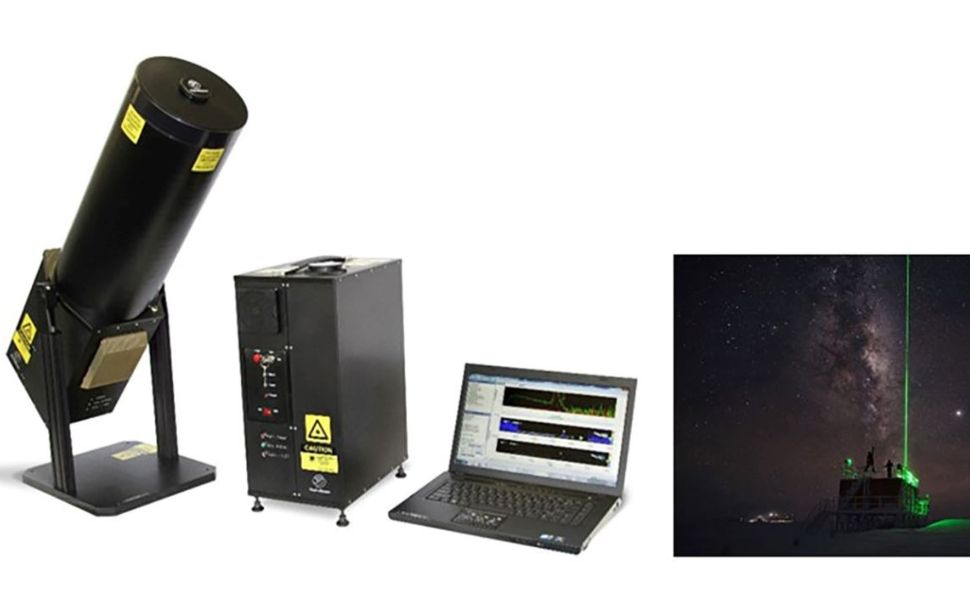

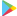
Micropulse Lindar mini ground remote sensing system
This is the only device capable of long-range monitoring exceeding 10 kilometres, and it actively scans air layers to detect pollution components. Compound concentrations in air layers can be determined using the idea of varying light absorption amongst pollution components. Lindar systems can capture real-time data, enabling long-term monitoring of pollutant concentrations.
Lidar is a novel technology that is based on radar technology. This method employs laser beams with wavelengths ranging from UV to near-infrared that may be scanned in the visible light range (visible region), allowing researchers to examine gas aerosols and fine particles in several levels of the atmosphere.
It will be simple to compute the concentration of pollution in the atmosphere's layers using the absorption principle and wave scattering. Meanwhile, radar, in general, and weather radar, in particular, only employ microwaves (long waves such as UHF and VHF), allowing them to detect only large clouds and fog, which are often disturbed due to their proximity to radio wavelengths.
Air monitoring uses laser-based optical measurement equipment, known as Lidar, to study climate change and atmospheric physics. It can measure dust density, aerosols, ozone, and toxic emissions like mercury, SO2, NO2, and benzene. LIDAR technology is used by numerous global networks, including NASA's MPLNET, Aerosol Research Lidar Network (EARLINET), Asian Dust Network, and Aerosol Monitoring by Lidar (AD-Net).
Lidar technology offers data on clouds and atmospheric surface boundary layers up to 15 km altitude, enabling co-polarized and polarised backscatter measurements. It also provides information on the aerosol phase, allowing the calculation of concentration distribution and properties in the vertical direction.
Investing in a Micro Pulse Lidar (MPL) system aims to address high levels of urban pollution caused by temperature inversion. This technology will be used to monitor long-range air pollution in critical economic regions, such as Ho Chi Minh, and improve air pollution warning forecasts in cities like other significant cities in the future. This technology is based on science and practice in various countries worldwide.
Source: Following by MONRE wrote on 26/04/2024, https://monre.gov.vn/Pages/ung-dung-cong-nghe-lidar-trong-quan-trac-o-nhiem-khong-khi.aspx, accessed in 08/05/2024