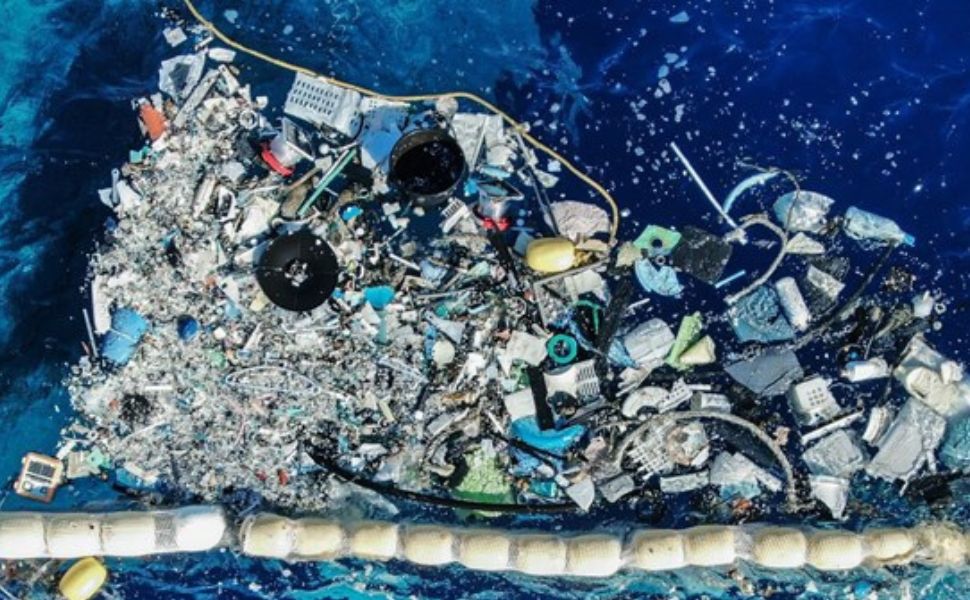
Moving towards coastal plastic waste monitoring with remote sensing technology in Vietnam
In order to improve the efficiency of management and monitoring of plastic pollution in the sea and coastal areas, the National Remote Sensing Agency is implementing the project "Monitoring coastal plastic waste by remote sensing technology." Nguyen Quoc Khanh, Director General of the National Remote Sensing Agency, said that the monitoring will allow state management agencies and local authorities to promptly detect and conduct large-scale monitoring of large dumps and clusters of plastic waste as well as their impacts on the ecological environment.
The project is expected to contribute to improving the efficiency of management and monitoring of plastic pollution in the sea and coastal areas. In addition, with advanced technological methods and processes, the project will allow state management agencies and local authorities to promptly detect and conduct large-scale monitoring of large plastic waste dumps and clusters as well as their impacts on the ecological environment.
According to Mr. Nguyen Quoc Khanh, Director General of the National Remote Sensing Agency, remote sensing technology using images taken from space with a large coverage area, higher and higher frequency of repeated shooting, providing information collected on many different spectral channels will be an effective tool to support and overcome some limitations of direct monitoring at sea.
In addition, because SAR remote sensing data is very sensitive to the roughness of plastic waste clusters compared to the surrounding surface, it can be exploited to detect, draw and monitor areas with plastic pollution. SAR image data can also be a useful tool for detecting and monitoring microplastic components.
According to the study, plastic materials floating in the sea will create habitats for microorganisms. The activity of microorganisms on the surface of plastic matter will create biofilms and streaks (dark patches). These biofilms and streaks are visible on radar images (dark patches on black-and-white radar images), but not recognizable on optical images.
Illustrations
Therefore, the combined use of different types of remote sensing image data and direct survey data at sea is a very feasible and highly effective option in monitoring plastic pollution at sea. Through monitoring the dispersal of plastic waste into the sea from various sources, such as land through river systems, coastal socio-economic activities, marine activities and the movement of waste from the ocean and adjacent waters into the East Sea of Vietnam.
On the other hand, remote sensing methods are considered suitable and effective when used for early detection and classification of plastic waste at sea due to the marked difference in the spectral reflection of plastic waste compared to the surrounding environment. The characteristics of the shape and structure can also be used in the identification of plastic waste in the sea.
"With the application of remote sensing data processing technical solutions combined with simulation models, it will significantly reduce the sampling survey at sea, contributing to reducing the cost of labor, equipment and vessels. In particular, the project will contribute to improving the efficiency of management and monitoring of plastic pollution in the sea and coastal areas, allowing state management agencies in charge of the environment such as the General Department of Environment, the General Department of Seas and Islands, the Departments of Natural Resources and Environment and local authorities, to promptly detect and conduct large-scale monitoring of dumps, large clusters of plastic waste as well as their impact on the ecological environment" – Mr. Nguyen Quoc Khanh emphasized.
Source: Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment