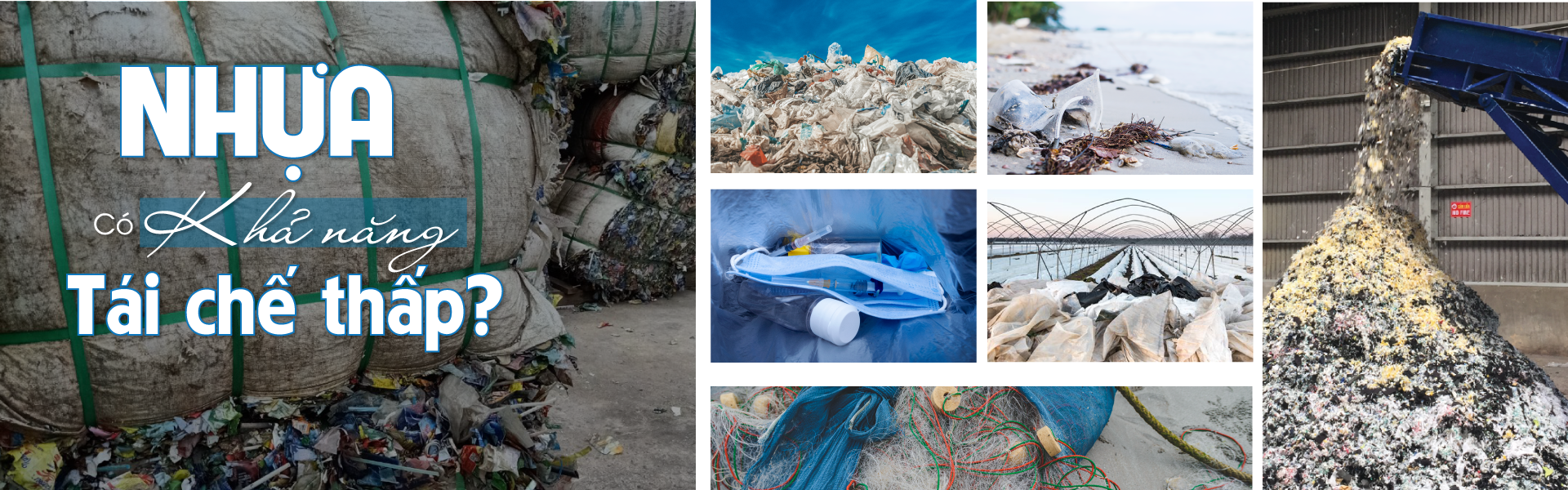
“Low-value plastics” in Vietnam: from waste to an alternative fuel!
Plastics with low value or low recycling potential are suitable for pre-processing (cutting, crushing) to become a source of input fuel to replace coal ... With experience - resources, A Chau Environment has full deployment capacity and is ready to receive plastic sources, in order to support the Units in achieving the aim of solid waste management and sustainable development in accordance with Vietnam's development priorities for the circular economy.
Introduction
What is the origin of low-value plastics?
From individuals and households in general activities
Activities for event planning, schools/educational institutions,…
Coffee chains, food and beverage stores, fast food restaurants, convenience stores,...
Market, shopping center,…
Tourism activities, restaurants, hotels, resorts,...
Medical examination and treatment facilities' activities
Agricultural production, fishing - aquaculture - seafood on river and the sea,...
Enterprises, manufacturing - business - service establishments,…
...
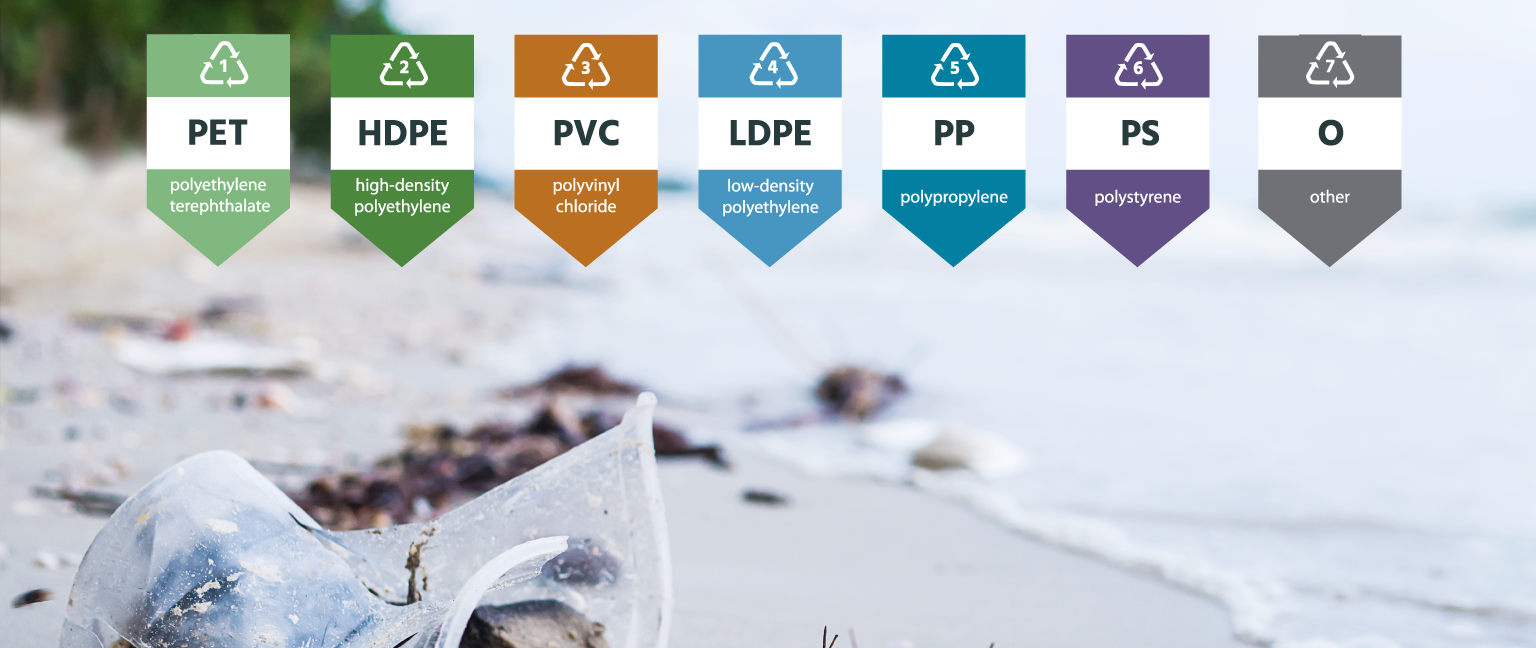
Identifying “low recycled plastics”: a guideline for recognition and classification
1. PETE OR PET – This is one of the most commonly used plastics in consumer products and is found in most soft drinks, mineral water, bottles, jars, food packaging/containers. PET is a completely recyclable material from bottle to bottle.
2. HDPE - This plastic is made from petroleum, is used to make shampoo/detergent bottles, water pipes, picnic tables, plastic chairs and cosmetic packaging...
3. PVC - This synthetic plastic polymer is used to make a variety of products, including pipes, doors, bottles, toys for kids and medical equipment.
4. LDPE – This is used to make various containers, dispensing bottles, cosmetic bottles, straws, plastic bags.
5. PP - A mechanically strong material, this is a manufactured commodity plastic and it is commonly used in the packaging and printing industries.
6. PS - This is a material that is frequently used to create foam packaging to protect products, lids, bottles, trays, lunch boxes, disposable cutlery and single-use plastic items.
7. PC - This plastic is commonly used in industrial products.
Impacts of plastic waste:
On February 22, 2022, data from the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) revealed that 460 million tons of plastic were used globally in 2021, more than double the amount used in 2000.
Plastics in general and plastics with low recycling value in particular currently have a very low recycling rate. The world generated 353 tons of plastic waste in 2021, just 9% of that material was recycled, 19% of that was destroyed, and roughly 50% was buried in qualified landfills. 22% of plastic waste was buried illegally, burned in open-air landfills, or released into the environment. A lot of plastics have spilled into the aquatic environment, with 1.7 million tons of plastic drifting into the ocean in 2019.
Plastic waste in the ocean is estimated to be 30 million tons, with another 109 million tons accumulating in rivers.
Low-value plastics: from being forgotten waste to resources – alternative materials, fuel!
According to the properties, it can generate heat and either has a low or no recycling value. "Co-processing" is a technology behind the recycling solution in the sustainable waste management tower. Co-processing uses non-recyclable waste as raw materials for production by taking advantage of capabilities from cement kilns to burn waste in order to replace traditional fuels such as coal, raw materials from waste are burned at temperatures up to 2,000 degrees Celsius. The residual ash will also be combined with clinker to create cement at the same time. The solution does not remove any waste during co-processing.
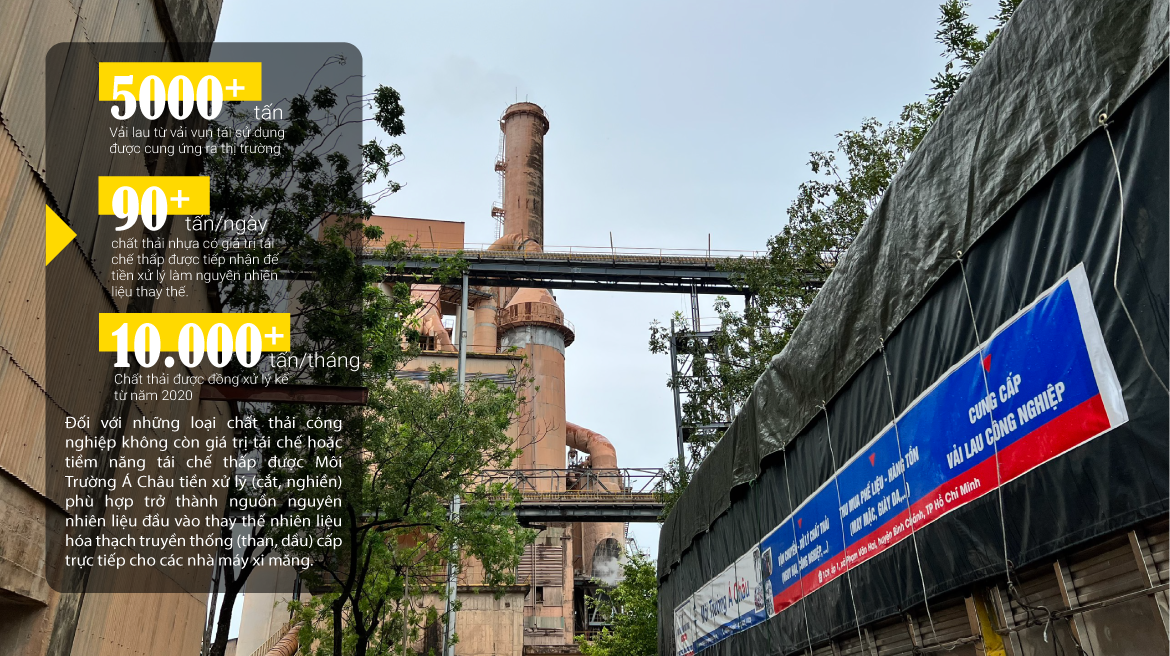
SOME SOLUTIONS FOR REUSING AND RECYCLING WASTE OF A CHAU ENVIRONMENT
- In an effort to reduce and increase the separation rate - recover value from waste in general, and sustainable solutions for non-recyclable (or low-recyclable value) plastic waste sources in particular, A Chau Environment strives to participate and collaborate more deeply with Partners, Agencies/Organizations, Units,... in order to jointly promote strengths and add value to the parties and the community.
- With experience and resources (human - material, network, legality,…), A Chau Environment is fully capable of deploying and ready to receive the above plastic sources, suitable pre-processing into alternative fuels, supports the Units in achieving the goal of solid waste management and sustainable development, in line with Vietnam's development orientation of the circular economy.
Plastic waste: managed in legal policy
The Law on Environmental Protection 2020 includes provisions for the prevention and control of ocean plastic waste pollution, the reduction, reuse, recycling, and treatment of plastic waste, as well as a roadmap for limiting the manufacturing and import of single-use plastic products, microplastic-containing products and goods, as well as single-use, non-biodegradable plastic packaging. The Law stipulates that organizations and individuals manufacturing and importing products and packages on the list of regulated recycling must comply with the compulsory recycling rates and specifications; regulations on waste classification, collection, reuse, recycling – EPR shows that the responsibility of the manufacturers do not stop at the product, but also extends to the management of post-consumer waste.
Resolution No. 55-NQ/TW on orientation of Vietnam's national energy development strategy to 2030, vision to 2045;
Decision No. 491/QD-TTg dated May 7, 2018 of the Prime Minister approving the adjustment of the National Strategy on integrated solid waste management to 2025, with a vision to 2050;
Decision No. 1746/QD-TTg dated December 4, 2019 of the Prime Minister on promulgating the National Action Plan on ocean plastic waste management to 2030;
Decision No. 175/QD-TTg dated February 5, 2021 of the Prime Minister approving the Project "Strengthening propaganda on plastic waste prevention and control in the 2021-2025 period";
Decision No. 1316/QD-TTg dated 22/7/2021 of the Prime Minister approving the Scheme to strengthen the management of plastic waste in Vietnam;
Directive No. 33/CT-TTg dated August 20, 2020 of the Prime Minister on strengthening the management, reuse, recycling, treatment and reduction of plastic waste;
Directive No. 41/CT-TTg dated December 1, 2020 of the Prime Minister on a number of urgent solutions to strengthen solid waste management;
Vietnam's commitments at COP26;
Our regional Customer & Partner services center in Vietnam:
Northern Services Center: 033 8351122
Central Services Center: 0902 450585
HCMC – Eastern Services Center: 033 8351122
Southern Services Center: 0902 912586